Nutrition tips
All you need to know about food allergy

By: Dana Al Salah – Certified Food Allergy Coach
What is an allergy?
Allergy is an immune response to a normally harmless substance.
People can be allergic to many things such as pollens, molds, dust mite, animal dander or saliva, insect stings or bites, medication, food, latex etc.
What is a food allergy?
A food allergy is an immune system disease. The body’s immune system reacts to a food protein because it mistakes that food protein as a threat. Symptoms can vary from mild to severe which could be life-threatening; anaphylaxis.
What is the difference between food allergy and food intolerance?
Food allergy is sometimes confused with food intolerance. Food allergies involve your immune system and can be life-threatening. An intolerance is when your body has trouble digesting a food. It can make you feel bad, usually with an upset stomach, but it is not life-threatening. The most common intolerance is to lactose—which is a natural sugar found in milk.
What are the most common food allergens?
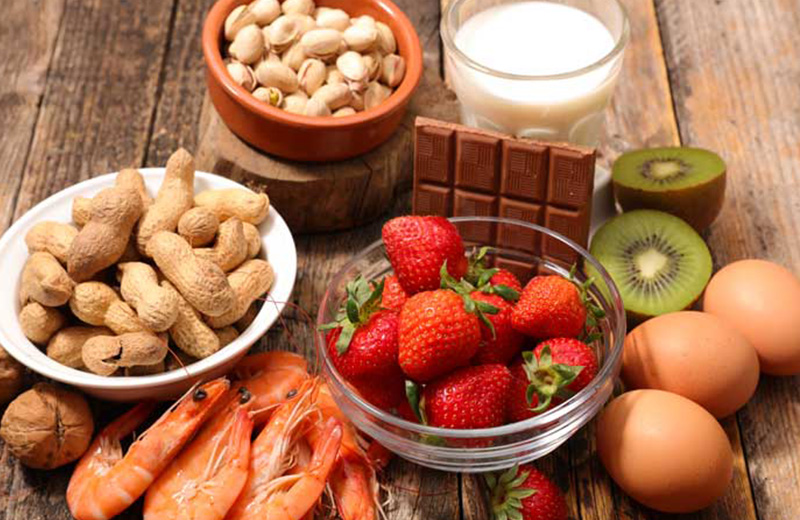
All food can cause a reaction. More than 170 foods are known to cause food allergies.
The most common foods that ta cause food allergy reactions are milk, eggs, peanuts, tree nuts, soy, wheat, fish, shellfish, and sesame.
What are the symptoms of a food allergy reaction?
An allergic reaction to food can have many different symptoms, and a single person can experience different symptoms from one reaction to the next. Many reactions start with skin symptoms, like hives or a rash, but some do not. More serious symptoms like a drop-in blood pressure and trouble breathing can be life-threatening.
Potential signs and symptoms of an allergic reaction:
- Mouth: Itchy, swelling of tongue and/or lips
- Throat: Itchy, tightness/closure, hoarseness, trouble breathing/swallowing
- Skin: Itchy, hives, redness, swelling, red watery eyes
- Gut: Nausea, vomiting, cramps, diarrhea
- Lung: Short of breath, wheeze, repetitive cough
- Heart: Pale or blue skin color, dizzy/faint, weak pulse
- Neurological: Sense of “impending doom,” irritability, change in alertness, mood change, confusion
- Other: Itchy, red, watery eyes
What is anaphylaxis?
Anaphylaxis “A-na-fi-LAX-is” is a serious life-threatening allergic reaction that comes on quickly.
Early use of an epinephrine auto-injector is the primary treatment for anaphylaxis.
Will antihistamines stop anaphylaxis?
No. While antihistamines can help relieve some mild symptoms from an allergic reaction, such as an itchy mouth or hives, they cannot stop the life-threatening symptoms of anaphylaxis.
How much of a food allergen does it take to cause a reaction?
Even trace amounts of a food allergen can cause a reaction in some people with food allergies. Although ingestion is the primary cause of severe reactions, in some cases, skin contact or breathing in a food protein (e.g., steam from cooking shellfish) can cause symptoms.
How long does it take for a reaction to start after eating a food?
Symptoms usually start appearing a few minutes to two hours after eating a food. In some cases, the second wave of symptoms may come back after the first symptoms have gone away. This is called a biphasic reaction. The risk of a biphasic reaction is why patients who suffer a severe reaction should remain at a hospital or under medical supervision for four to six hours for observation.
Is there a cure for food allergy?
Not yet. Strict avoidance of the food allergen is the only way to prevent a reaction and an epinephrine auto-injector is the only medicine to stop a severe reaction called anaphylaxis.
Can a person outgrow their food allergies?
Most children outgrow their food allergies, especially with milk. Peanut, tree nut, fish and shellfish allergies usually are lifelong.
What should you do if you think you or any family member think to have a food allergy?
If you think you or one of your family members have a food allergy, you should talk to your GP, allergist or a medical practitioner with experience in food allergy.
Why are food allergies increasing?
Food Allergies Are on the Rise. The Centres for Disease Control & Prevention reports that the prevalence of food allergy in children increased by 50 percent between 1997 and 2011.
Most experts do believe that there’s a clear increase in food allergies. Surely, diagnoses have upgraded over the last years, therefore, some of the increase may be attributed to better diagnoses.
No one really knows why food allergies are on the rise. One theory, known as the “hygiene hypothesis” we are being too clean!
Some studies suggest that change in weaning practices and introducing solid foods over the last decades may be part of the cause. Recent research in England shows that early ingestion of peanuts may help prevent the development of peanut allergy. Nevertheless, you should always seek advice from your specialist or allergist, for there are important warnings and guidelines to be advised
Other theories suggest that our diet and the modern lifestyle in addition to antibiotics and vaccinations may be responsible for the rise. Global warming seems to be part of the cause. Genetics also play a major role in the development of food allergies; for example, if one parent has allergies, their child has a greater risk of developing allergies as well.
More studies are yet to be made to try to understand more about the complexity of food allergies and more importantly finding a cure.